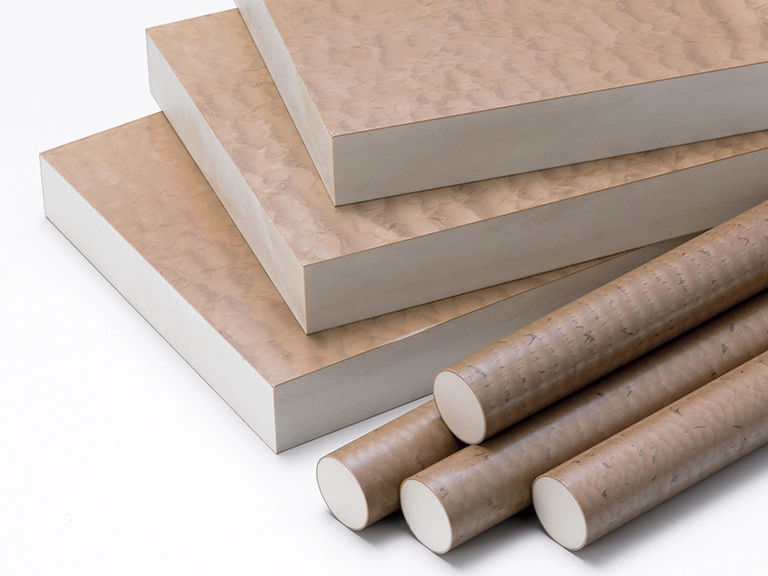


Glass Transition Temperature : ~85°C
Melting Point : ~280°C
Continuous Use Temperature : Up to 200°C in most applications.
Thermal Stability : High resistance to heat and thermal degradation.
Tensile Strength : ~70–90 MPa (varies by grade).
Flexural Modulus : ~3–4 GPa.
Wear Resistance : Excellent under dynamic conditions.
Dimensional Stability : Minimal shrinkage and creep.

Resistant to acids, bases, fuels, and solvents.
Hydrolysis Resistant : Performs well in wet or humid conditions.
High dielectric strength and insulation performance.
High dielectric strength and insulation performance.

Flame Retardancy: UL 94 V-0 rated without additives.
Low Outgassing : Suitable for vacuum applications.
Get Your Quote or Call : +91 99788 23122

Inert to most chemicals, fuels, and solvents.

Excellent stability under continuous high temperatures.

Retains rigidity and strength under stress.
Low coefficient of thermal expansion.

Inherently flame retardant.

A high-performance alternative to metals.

– Components for fuel systems and exhaust systems.
– Gears, bearings, and electrical connectors.
– Sensors and engine components.
– High-temperature electrical connectors and sockets.
– Substrates for printed circuit boards.
– Insulators for electronic components.

– Lightweight structural components.
– Seals and connectors for extreme conditions.

– Pump housings, valves, and pipes.
– Components for harsh chemical environments.

– Wear-resistant parts for machinery.
– Heat-resistant components for manufacturing equipment.
Components for renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind turbines.

High-performance parts for diagnostic and analytical equipment.
FDA-compliant grades for high-temperature food handling

Durable and lightweight components in household appliances.

Components in high-precision laboratory equipment.

We are fully equipped with latest manufacturing instruments and well qualified technocrats.



Plot No. 33, Survey No. 238, B/h Vikas Export, Gondal Road, Kotharia, Rajkot-360022
(Gujarat - India)
Copyright @ 2025 Vandit Polycraft PVT. LTD. All Rights Reserved | Website developed By : Impex Infotech